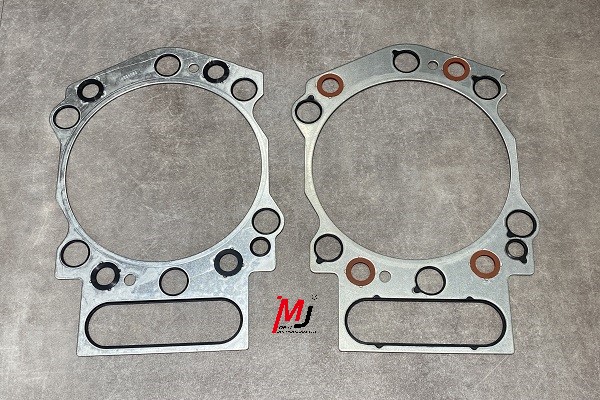
The thickness of a cylinder head gasket defines the distance between the cylinder head and the engine block. Most engines use a standard gasket thickness, but you’ll also find a few oversized head gaskets. At first glance, they may look identical, but oversized versions often have notches or small holes to mark their thickness.
Using the wrong thickness can lead to compression loss or even engine failure. That’s why understanding when to use an oversized head gasket really matters.
Why Do Head Gaskets Come in Different Thicknesses?
An oversized head gasket is typically used to correct deck-height problems or warpage on the cylinder head. When the head or block has been resurfaced or the engine has overheated, the original distance between the two changes. A thicker gasket compensates for the missing material, restoring proper compression and sealing.
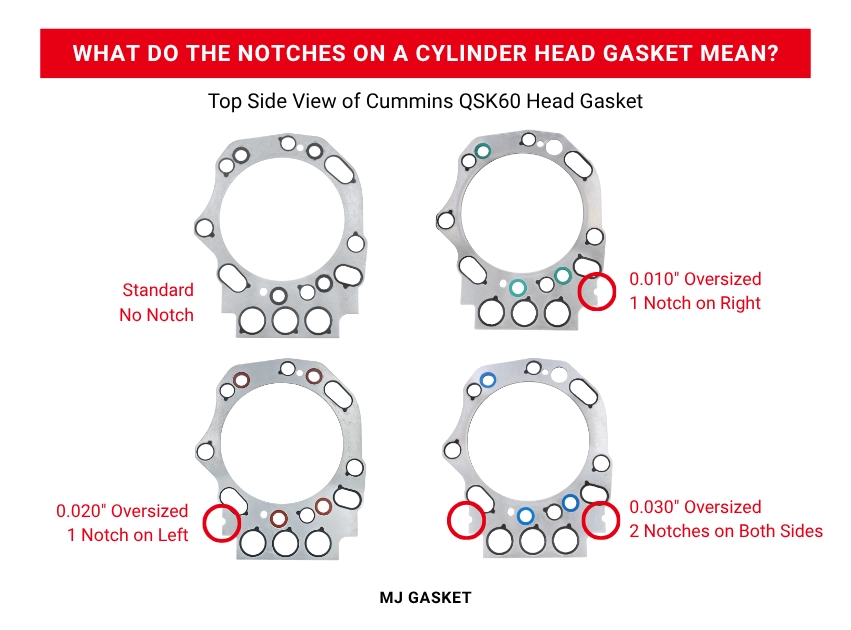
What Do the Notches on a Cylinder Head Gasket Mean?
At first glance, gaskets of different thicknesses may appear nearly identical, their shape, bolt pattern, and overall layout often look the same. However, the difference lies in small but important details that help identify the correct one for your engine. Manufacturers typically use unique part numbers for each thickness, ensuring precise identification in service manuals or parts catalogs. In addition to that, some gaskets feature holes, notches, or stamped marks along the edges to indicate their specific thickness.
Take a look at the images below, you can see how the Cummins QSK60 head gaskets differ in thickness, each one marked with a different set of notches to show its size.
These markings allow engine builders and technicians to quickly recognize the correct gasket before installation, preventing costly mistakes caused by mixing up standard and oversized versions.
In summary:
- OEMs assign different part numbers for gaskets of various thicknesses.
- Some gaskets include holes, notches, or stamped marks as identification indicators.
Is an Oversized Head Gasket Always Necessary?
No, an oversized head gasket is not necessary for most engines. In the majority of cases, a properly sized standard head gasket will provide the proper seal between the cylinder head and engine block, with no negative effect on performance or reliability.
Installing an oversized head gasket in an engine that doesn’t require it can actually have adverse effects on performance and reliability, so it’s important to consult with a qualified mechanic or engine builder to determine whether an oversized gasket is needed for your specific engine.
What Happens If I Use a Thicker Head Gasket?
A thicker (oversized) head gasket helps recover compression height after machining, keeping pistons from hitting the head under high-load operation. But if the head and block have not been machined, a thicker gasket will actually lower the compression ratio, softening engine response and power output.
Oversized Head Gasket
When it comes to Cummins engines, several cylinder head gasket thickness options are available to match different repair and rebuild conditions. Each gasket thickness is carefully specified to restore or maintain the correct compression height after machining or component wear. A standard head gasket is typically used for untouched engines, while oversized head gaskets, often labeled with “+0.10 mm”, “+0.25 mm”, or “+0.50 mm”, are designed to compensate for the amount of material removed from the cylinder head or block during resurfacing.
Below are some commonly referenced Cummins head gasket thicknesses for popular heavy-duty models:
Cummins N14/NT855 Standard Head Gasket and Oversized Head Gasket
For the Cummins N14/NT855, there are 4058790 as the standard version and 3098985 is the oversized version.
- 4058790: Standard
- 3098985: 0.010″ Oversized
Cummins QSK19/QSK38 Standard Head Gasket and Oversized Head Gasket
For the Cummins QSK19/QSK38, there are 4334080 as the standard version and 4334081 is the oversized version.
- 4334080: Standard
- 4334081: 0.020″ Oversized
Cummins QSK50/QSK60 Standard Head Gasket and Oversized Head Gaskets
For the Cummins QSK50/QSK60, there are 3649981 as the standard version and 3649982, 3651085 and 3651086 are the oversized version.
- 3649981: Standard
- 3651085: 0.010″ Oversized
- 3649982: 0.020″ Oversized
- 3651086: 0.030″ Oversized
Cummins B5.9/B6.7 Standard Head Gasket and Oversized Head Gasket
If you’re working with Cummins B5.9 or B6.7 engines, you may already know that picking the right head gasket thickness makes a big difference. In our article Choose the Right Cummins Head Gasket, we explained how both standard and oversized head gaskets play important roles.
If you’d like to learn more about oversized head gaskets for other engine brands or models, please share your OEM part numbers with us.
Quick FAQ about Oversized Head Gasket
What does a thicker head gasket do?
A thicker (oversized) head gasket compensates for material removed during machining or resurfacing, bringing the cylinder head–to–block distance back to factory spec. This restores the correct compression height and prevents piston-to-head contact under high load, especially important for rebuilt or high-mileage engines.
Is it better to have a thinner or thicker gasket?
Neither is “better”, it depends on your engine’s condition.
A standard gasket works best for engines that haven’t been machined or resurfaced, keeping compression and performance within factory specs.
A thicker (oversized) gasket is ideal when the cylinder head or block has been machined, as it restores the proper deck height and compression ratio. Choosing the wrong thickness can affect sealing and combustion efficiency, so always match the gasket to your engine’s current measurements.
Does a thicker head gasket raise compression?
No, a thicker head gasket actually lowers compression.
Because it increases the distance between the piston and the cylinder head, the combustion chamber volume becomes slightly larger, resulting in a reduced compression ratio. On the other hand, a thinner gasket decreases chamber volume and slightly raises compression. Selecting the right thickness is key to maintaining the manufacturer’s intended compression ratio and engine performance.